AI in personalised medicine: Better risk identification, prevention and treatment of carotid artery disease
Carotid artery disease is caused by the narrowing or blockage of the neck arteries due to plaque build-up (atherosclerosis). Current screening for asymptomatic carotid disease, prevention of stroke and disease management rely on the 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines of the European Society for Vascular Surgery. However, disease variability impedes effective clinical decision-making, necessitating more personalised interventions.
AI-based patient stratification strategy
The key objective of the EU-funded TAXINOMISIS project is to develop a novel model that can be employed to categorise patients based on their risk of developing carotid artery disease and experiencing cerebrovascular events manifested as stroke, transient ischaemic attack or transient loss of vision. The model will assist healthcare professionals in making better-informed decisions about patient care and treatment, potentially leading to improved clinical outcomes. “TAXINOMISIS has designed a rational new approach to address key clinical gaps in carotid artery disease in terms of predicting progression, need for follow-up and selection of appropriate interventions,” explains project coordinator Dimitrios Fotiadis. The model encompasses AI-based modules/components that integrate clinical information and personalised patient data, plaque and brain images, along with blood flow patterns and novel biomarkers. Computer models and simulations predict silent brain lesions, cardiovascular events, plaque vulnerability, and plaque evolution and rupture.
Machine-learning techniques for carotid artery disease prediction
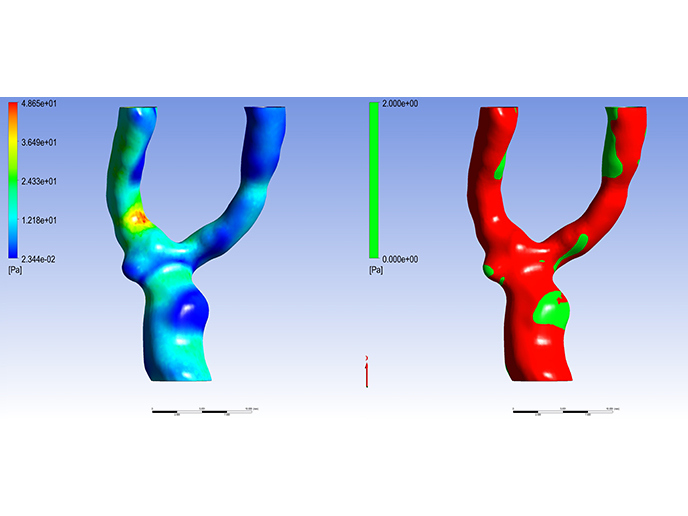
The TAXINOMISIS risk stratification tool assesses the risk of carotid artery disease in individuals by using non-imaging data as input to evaluate the likelihood of high-risk plaques and the potential development of the disease. The tool goes a step further by linking the condition of the carotid artery to the presence of brain lesions and predicting the risk of new brain lesions in patients. Furthermore, the TAXINOMISIS stratification tool includes a blood flow component, which is applied to predict the risk for plaque progression, while it is also exploited as an event prediction model. Additionally, the tool can estimate the risk of plaque rupture, which is a serious condition associated with blood clots inside blood vessels. The tool uses two different models to estimate the risk of plaque rupture – a complex model, which takes into account various factors related to both the structure of the arterial wall and the composition of the plaque itself, and a simplified model, which focuses only on the interior space of the artery, known as the lumen. Thus, medical professionals can choose the appropriate level of analysis based on the available data, resources, and the clinical context. Finally, the TAXINOMISIS risk stratification tool utilizes advanced AI techniques to reconstruct the 3D geometry of arteries and to characterize plaque through magnetic resonance and ultrasound imaging data.
Added value of AI in patient care
“We anticipate that the TAXINOMISIS risk stratification tool will increase the efficiency and quality of the overall health system on carotid artery disease,” outlines Prof. Fotiadis. The risk stratification tool may also aid medical professionals in comprehending the disease’s fundamental mechanics, which might eventually lead to better treatment plans. By speeding up the diagnosis process and reducing the need for more intrusive tests or treatments, the TAXINOMISIS tool will also contribute to lower healthcare expenditures. With input from physicians and users, as well as data from clinical trials and real-world cases, the team will further improve the platform’s algorithms and models. Joint ventures or collaborations with other organisations will be instrumental to integrating the TAXINOMISIS tool in healthcare systems or combining it with other available tools. “We envision the TAXINOMISIS tool to be incorporated in daily clinical practice, enhancing clinical decision-making through accurate risk stratification,” concludes Prof. Fotiadis.
Keywords
TAXINOMISIS, carotid artery disease, AI, brain lesion, patient stratification, stroke, biomarkers, blood flow, plaque rupture, haemodynamics