Cars of the future
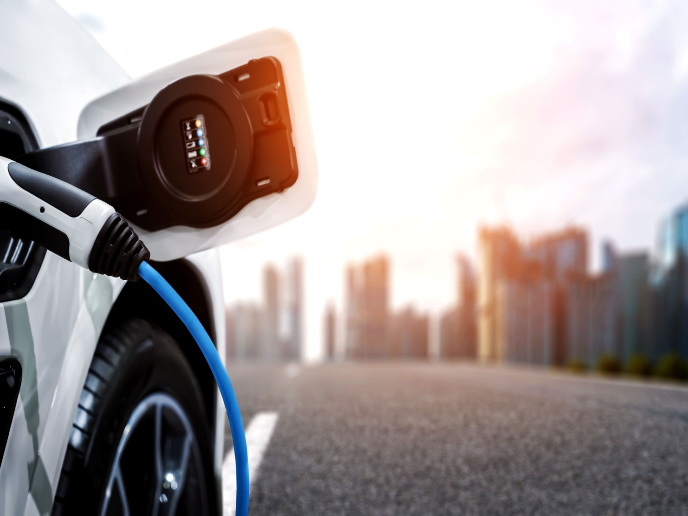
It has long been a world dream to create non-polluting electric vehicles based on super-efficient batteries. The EU-funded project 'Sustainable batteries' (SUBAT) investigated the battery market to help boost sustainable transport in the future for the EU. Three European universities and four stakeholder organisations came together to assess current and future battery technologies worldwide. The consortium did not involve any supplier or manufacturer of batteries in order to guarantee the project's neutrality. It closely assessed energy, power, life cycle, costs, temperature, charging, maintenance, safety and efficiency of battery systems, as well as recyclability, energy efficiency and commercial viability. SUBAT analysed all batteries in the context of battery-electric and hybrid vehicles. It considered necessary peripheral systems as well as the battery management system, which plays an important role in battery performance. The project team also identified the best software to analyse the life-cycle of different batteries. In the first stage of the project, SUBAT compiled a comprehensive technical overview of battery technology that could prove very useful to stakeholders. It then conducted a full environmental assessment of industrial battery systems taking the nickel-cadmium battery as a benchmark. The project team then conducted a cost assessment for the industry and consumers, analysing factors that raise battery costs for users. They also compared the European vs. non-European markets in battery sales and trade balance. On the green front, SUBAT analysed emissions of potentially harmful substances and resources consumed, enabling better comparisons between systems and batteries. At the end, the project produced an overall assessment of the battery technologies. It ranked environmental, technical and economic parameters in an objective way considering different perspectives with regard to consumers, manufacturers and the political environment. These studies will be of use to all manufacturers, suppliers and consumers, helping them identify the best road forward and bringing Europe a step closer to energy-efficient, eco-friendly electric cars.